

Its other function is to protect the non- malignant cells in the body.
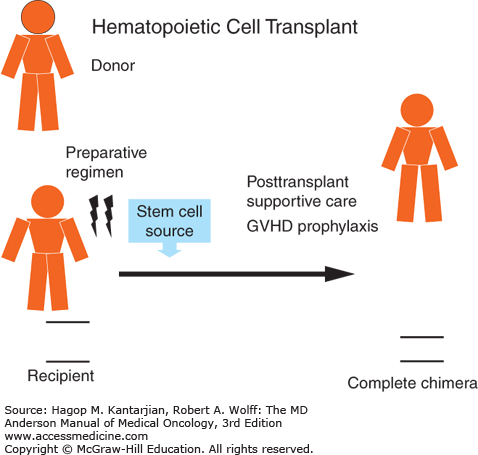
In stem cell transplantation, the stem cells with suitable advanced characteristics are administered so that they develop into immunological cells capable of destroying cancer cells. Stem cell transplantation is a technique mainly used in the treatment of cancer. But improvements in the way the cells are prepared and matched and in the care of the person after the transplant have helped reduce problems.The key difference between autologous and allogeneic stem cell transplant is that, in autologous stem cell transplant, one’s own cells are used in transplantation, while in allogeneic stem cell transplant, a donor is matched prior to transplantation and then administered. Symptoms include swelling and tenderness of the liver, weight gain, jaundice, and fluid buildup in the belly.Ī transplant from an unrelated donor is more likely to cause problems. This is a serious liver problem caused by the high dose of chemotherapy or radiation given before a transplant. GVHD does not occur when an identical twin is the donor. GVHD is treated with medicine that lowers the activity of your immune system. GVHD affects the skin, gastrointestinal tract, and liver. After chronic GVHD occurs, it may take as long as 3 years to go away. If it happens after 3 months, it is called chronic GVHD. If it happens within 3 months, it is called acute GVHD. The new stem cells attack other cells in your body. If this occurs, the likelihood of a cure is low. The new stem cells don't work, or they work for a short time and then fail. Serious, long-term complications of an allogeneic transplant include: Recurrence of the disease that the transplant was used to treat.Infection, such as pneumonia, shingles, or herpes simplex.Bleeding, because of a severe decrease in red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.Waiting for the transplanted stem cells to produce healthy blood cells.Įarly complications of both allogeneic and autologous transplants usually occur within 5 to 10 days.Having chemotherapy (sometimes along with radiation) to destroy cancer cells or damaged stem cells.The new cells can come from the blood, bone marrow, or umbilical cord blood. The allogeneic transplant process includes: If your bone marrow is damaged or destroyed, it can no longer make normal blood cells.Ī stem cell transplant may be used to treat diseases that damage or destroy the bone marrow, such as non-Hodgkin lymphoma and Hodgkin lymphoma, leukemia, multiple myeloma, and aplastic anemia. Bone marrow stem cells turn into red blood cells, white blood cells, or platelets to help your body stay healthy. You also have some that circulate from your marrow into your blood. This is more likely when the donor is your brother or sister. The important thing is that the donor's immune system markers are closely matched to yours. When they come from another person, it's called an allogeneic stem cell transplant. The transplant can use stem cells that come from your own blood or bone marrow.

In a stem cell transplant, healthy stem cells are placed in your body through an IV to help your bone marrow start to work as it should.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
